ChatGPT сказал:

Legionnaires’ disease is a serious type of pneumonia caused by Legionella bacteria, which are found in water systems, and in medical literature it is placed within the broader category of legionellosis (which also includes Pontiac fever). Descriptions group the most severe manifestations of Legionnaires’ disease together with febrile illnesses linked to Legionella exposure. It is a potentially serious condition that can be life-threatening in some cases. Legionnaires’ disease is characterized as a form of pneumonia involving the lungs. Susceptibility varies, with certain populations discussed as having higher risk. Person-to-person spread is not considered the usual route; infection is described as occurring through inhalation of contaminated aerosolized water droplets.
Sources outline environmental contexts associated with exposure. Legionella bacteria inhabit warm freshwater and can amplify in man-made water systems when conditions allow. Reported settings include hot tubs, decorative fountains, cooling towers, large plumbing networks, and showers where aerosols can form. Recreational water venues are discussed in relation to maintenance practices and water temperature. Building water management and system upkeep are emphasized in public health discussions as relevant to controlling amplification and aerosol generation.

Clinical descriptions highlight symptoms consistent with pneumonia. Reports note high body temperature with chills, cough, headache, and myalgias or arthralgias. Weakness and fatigue are frequently mentioned. Temperatures can reach 104°F (40°C) in some cases. Early complaints may be nonspecific, such as mild headache or generalized malaise, followed by progression over one to two days to more pronounced respiratory and systemic findings in susceptible individuals.

Risk factors described in reviews indicate that not every exposed person develops disease. Higher likelihood after exposure is reported among people with a history of heavy tobacco use, individuals with conditions that compromise immune function (including advanced HIV infection), and those with chronic lung disease. Additional contexts include certain chronic medical conditions and older age groups, which appear more frequently in case series than in younger populations.
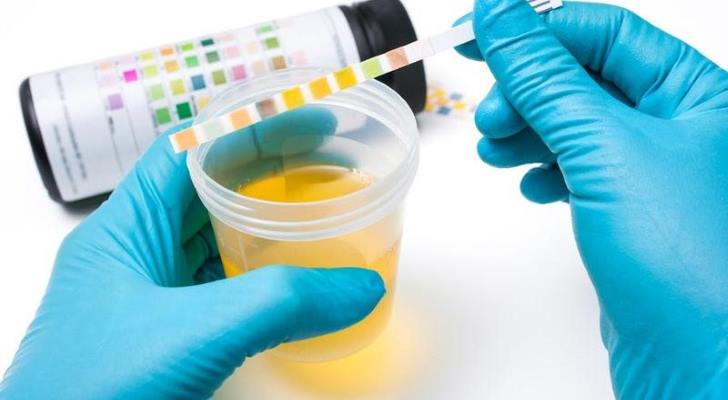
Clinicians evaluate symptom patterns and timing alongside targeted tests. Diagnostic approaches can include urinary antigen testing that detects Legionella pneumophila serogroup 1 antigen for identification. Blood samples and cultures contribute additional information. Imaging studies are used to assess pulmonary involvement. These tools are discussed as part of a diagnostic framework rather than as measures that alter immune defense directly.

Prevention topics in public health materials focus on water system management in buildings and healthcare facilities, including monitoring of temperature, disinfectant levels, and system maintenance to limit bacterial growth. Summaries also note that exposure occurs through inhalation of contaminated aerosols in warm water environments. The illness is contracted by inhaling contaminated water droplets and is not spread from person to person.
Learn more about Legionnaires’ disease at Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC).

