Impetigo Signs, Symptoms and Causes
What does the disease mean? Impetigo is a skin disease caused by the penetration into the hair follicles of Staphylococcus aureus, streptococcus or these bacteria simultaneously. The disease is characterized by high infectiousness. As a rule, children are under risk while adults are infected because of damage to the skin during shaving. Also, the disease can be a consequence of other skin problems, for example, severe itching.
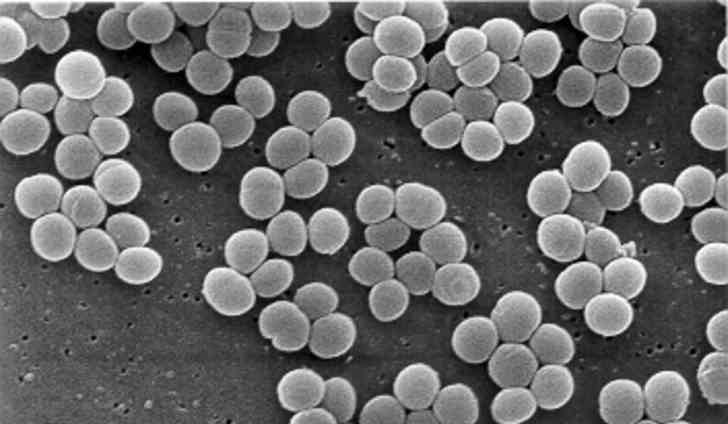
Why does Impetigo occur? As a rule, it is caused by staphylococci, sometimes streptococci, or a combination of both. These bacteria, mainly, are part of the microflora of the skin and are activated in case of a decrease in the protective function of the skin, and with a weakening of immunity. Most often impetigo affects the skin of the hands and face. Impetigo can be caused by one of two pathogens: Staphylococcus aureus and hemolytic streptococcus.

Staphylococcus aureus is a bacterium that is present in the body of 25-40% of people. It is found in the mucous membrane of the nose, throat, vagina. Staphylococcus aureus is a conditionally pathogenic microorganism. That is, it usually does not cause any diseases. But under certain conditions, staphylococcosis becomes pathogenic. It detects toxins that cause pathological changes in the organs and tissues of a person. Hemolytic streptococcus is also a conditionally pathogenic bacterium. Normally inhabits the mucous membranes of the mouth, nose, and throat of many people. Can isolate toxins that lead to pathological changes. It is the causative agent of many diseases, including impetigo, erysipelas, tonsillitis, etc.

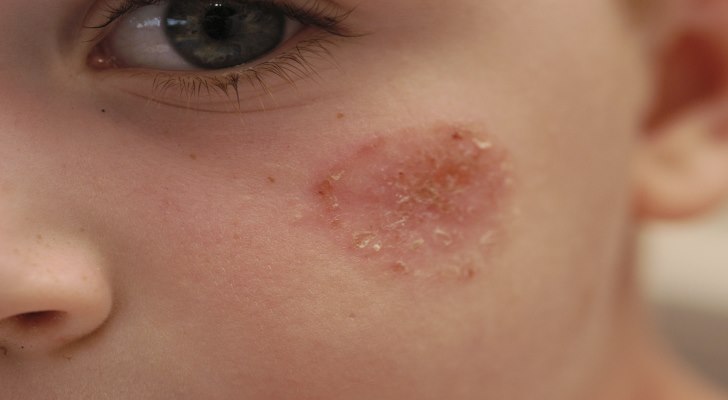
How to recognize Impetigo? Impetigo is characterized by the formation of small pimples rising above the surface of the skin (vesicles, or fliken), saturated with watery unclear contents or pus. These pustules are usually numerous, either of them is surrounded by an inflammatory corolla in the shape of a closed ring or semicircle.

Pustules, usually, are not too large, although in neglected variants they have all the chances to unite, covering the great areas of the skin, repeating the appearance of flat bubbles. As soon as they are opened, emphasizing the purulent contents, the skin becomes covered with a thick crust. After treatment, scarring does not remain, because impetigo affects only the superficial layers of the skin.

The danger of this disease is in fact that it is able to provide complications from the internal organs. Therefore, every impetigo outbreak is subject to scrutinous investigation. Factors that increase the likelihood of disease are skin damage; shaving a poor-quality razor that traumatises the skin; cracked skin; scabies (brushing on the skin); diabetes mellitus (leads to disruption of the blood supply to the skin and its damage); decreased immunity, chronic diseases, severe infections; constant hypothermia; abnormality of personal hygiene; metabolic disorders; increased skin pH. Often, infection occurs in the hospital during treatment of severe illness or after surgery.

How can you carry out Diagnosis? The diagnosis is made by a dermatologist by anamnesis, clinical manifestations. If there is any doubt, a diagnosis is made of dermatoscopy. Besides, specific methods of checkup are used: staining smears of exudate by Gram (visible cocci under a microscope) and seeding of the separated bullae on the flora. Self-diagnosis and self-medication are unacceptable taking into account the contagiousness of impetigo. Differentiated impetigo with chickenpox, dermatomycosis, herpes, sycosis, contact and herpetiform dermatitis.

What must you do to block Impetigo? Skin contamination is one of the factors that increase the risk of streptococcal and staphylococcal infections, so careful observance of personal hygiene is a must. An active way of life, playing sports, sufficient being in the open air – all this reduces the risk not only of impetigo but also of any infections.

Isolation of the patient and frequent wet cleaning with disinfectants will help to avoid infection. There is especially high risk among people with reduced immunity: children, the elderly, pregnant women. The body must receive every day all the substances necessary for the normal functioning of the immune system.
